Keywords:AI, LLM, Stanford AI Index Report 2025, photon AI processor breakthrough, Claude 3.5 Haiku implicit reasoning, Meta Llama 4 series models, Qwen2.5-Omni multimodal model
🔥 Focus
Stanford Releases 2025 AI Index Report: Stanford University has published the extensive 456-page “2025 AI Index” report, providing a comprehensive overview of the current state and trends in the AI field. The report indicates that the US leads in the number of model releases, but China is rapidly catching up in model quality, significantly narrowing the performance gap. Training costs continue to rise (e.g., Gemini 1.0 Ultra estimated at ~$192 million), while inference costs are dropping sharply. The carbon footprint of AI is becoming increasingly severe, with Meta’s Llama 3.1 training generating substantial emissions. The report also notes that many AI benchmarks are saturated, making it difficult to differentiate model capabilities, posing a new challenge dubbed the “human final exam.” Public data scraping is becoming restricted (48% of top-level domains limit crawlers), raising concerns about reaching “peak data.” Corporate AI investment is massive, but significant productivity returns are yet to be seen. AI shows immense potential in science and medicine, but practical application translation still requires time. On the policy front, US state-level legislation is active, particularly focusing on deepfakes, while the global level mostly sees non-binding declarations. Despite concerns about job displacement, public sentiment towards AI remains generally optimistic (Source: AINLPer)
Breakthrough in Novel Photonic AI Processors: Two papers published in Nature introduce new AI processors combining photonics and electronics, aiming to overcome performance and energy consumption bottlenecks in the post-transistor era. Singapore-based Lightelligence’s PACE photonic accelerator (containing 16,000+ photonic components) demonstrated computation speeds up to 1GHz and a 500x reduction in minimum latency, performing exceptionally well in solving Ising problems. US-based Lightmatter’s photonic processor (with four 128×128 matrices) successfully ran AI models like BERT and ResNet with accuracy comparable to electronic processors, and demonstrated applications like playing Pac-Man. Both studies show their systems are scalable and manufacturable using existing CMOS foundries, potentially driving AI hardware towards greater power and energy efficiency, marking a significant step towards the practical application of photonic computing (Source: 36Kr)
UC Berkeley Open-Sources 14B Code Model DeepCoder, Comparable to o3-mini: UC Berkeley, in collaboration with Together AI, has released DeepCoder-14B-Preview, a fully open-source 14B parameter code inference model with performance comparable to OpenAI’s o3-mini. The model was fine-tuned from Deepseek-R1-Distilled-Qwen-14B using distributed reinforcement learning (RL), achieving a Pass@1 score of 60.6% on the LiveCodeBench benchmark. The team constructed a training set of 24K high-quality programming problems and employed an improved GRPO+ training method, iterative context extension (from 16K to 32K, reaching 64K during inference), and ultra-long filtering techniques. They also open-sourced the optimized RL training system, verl-pipeline, which doubles the end-to-end training speed. This release includes not only the model but also the dataset, code, and training logs (Source: Xin Zhi Yuan)
🎯 Trends
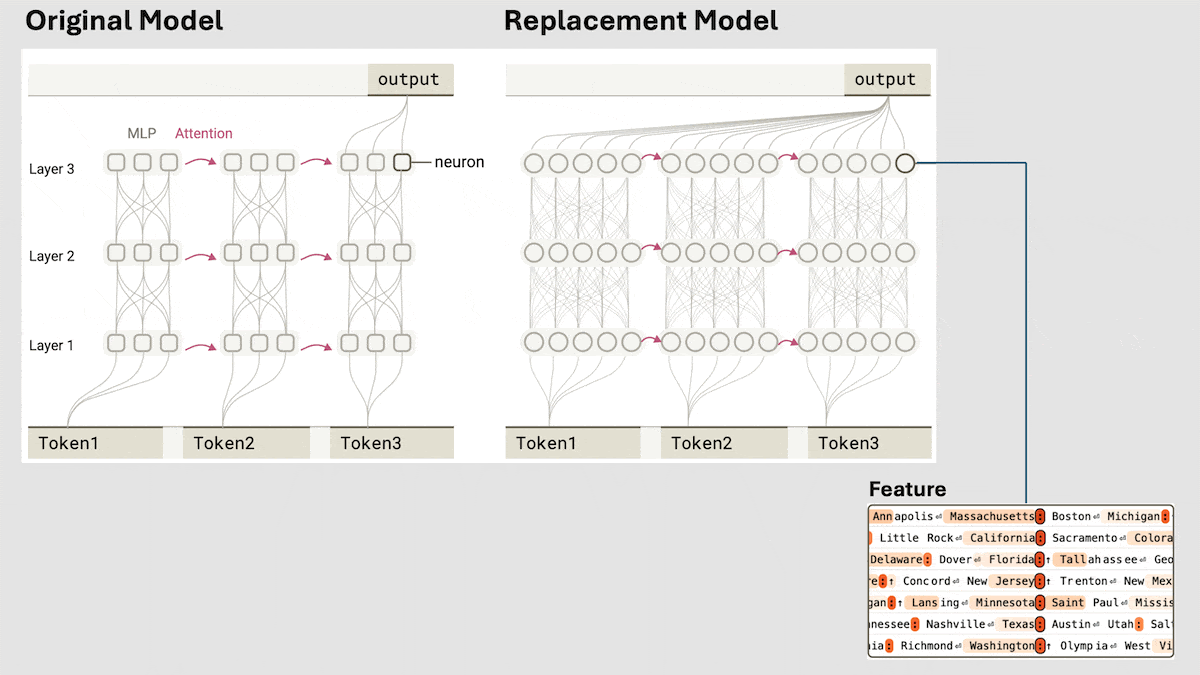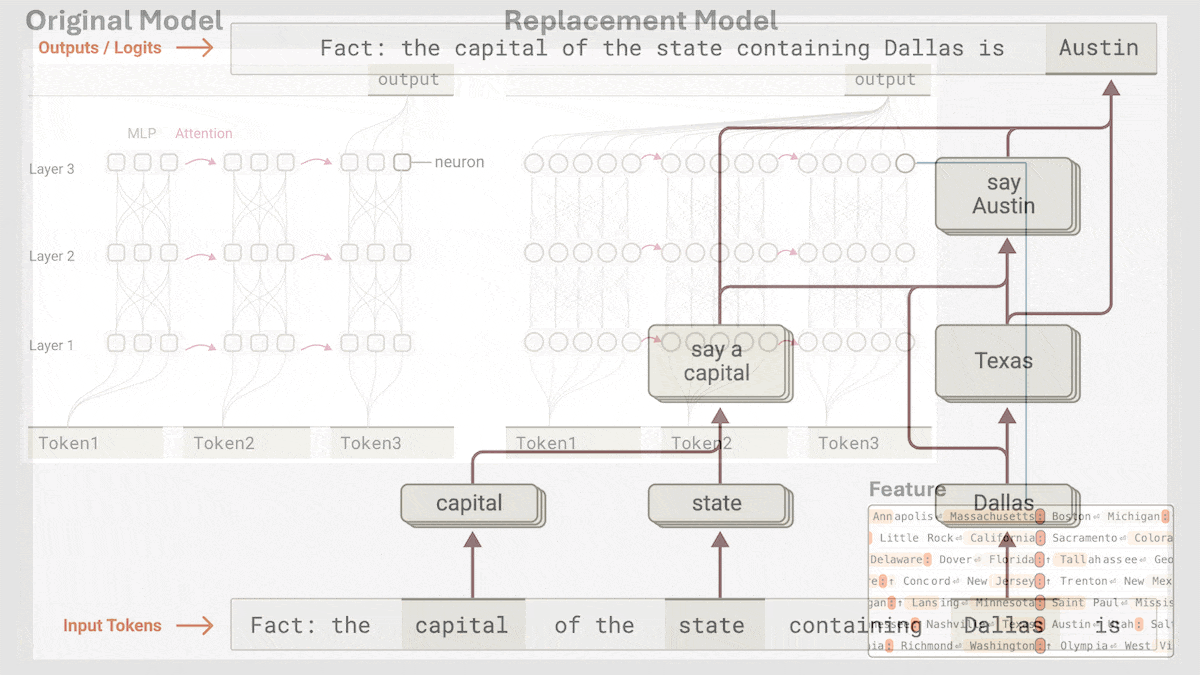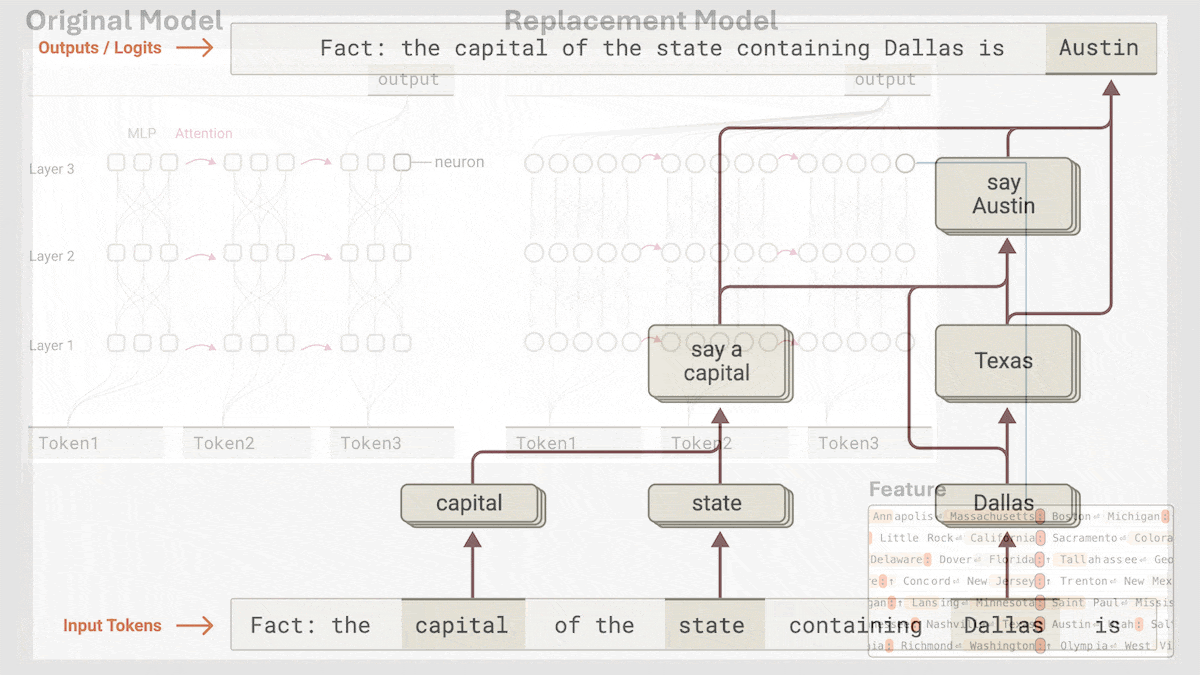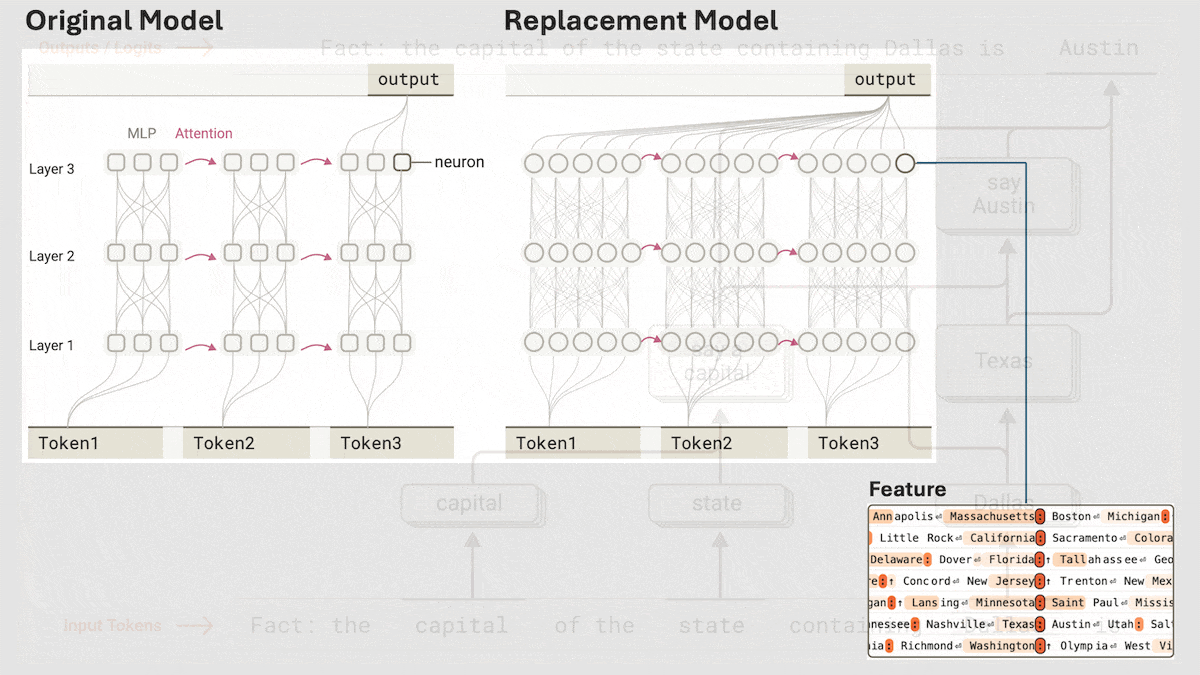
Anthropic Reveals Implicit Reasoning Mechanism in Claude 3.5 Haiku: Anthropic’s research team analyzed the internal workings of Transformer models (specifically Claude 3.5 Haiku) using a novel method. They discovered that even without explicit Chain-of-Thought training, the model exhibits reasoning-like steps through neuron activations when generating responses. The method replaces fully connected layers with interpretable “cross-layer transcoders” to identify “features” associated with specific concepts or predictions and constructs attribution graphs to visualize information flow. Experiments show that when answering questions (like “What is the opposite of small?” or determining the capital of the state Dallas is in), the model internally goes through multiple logical steps rather than directly predicting the answer. This research helps understand the inner workings of LLMs and distinguish genuine reasoning ability from superficial mimicry (Source: DeepLearning.AI)
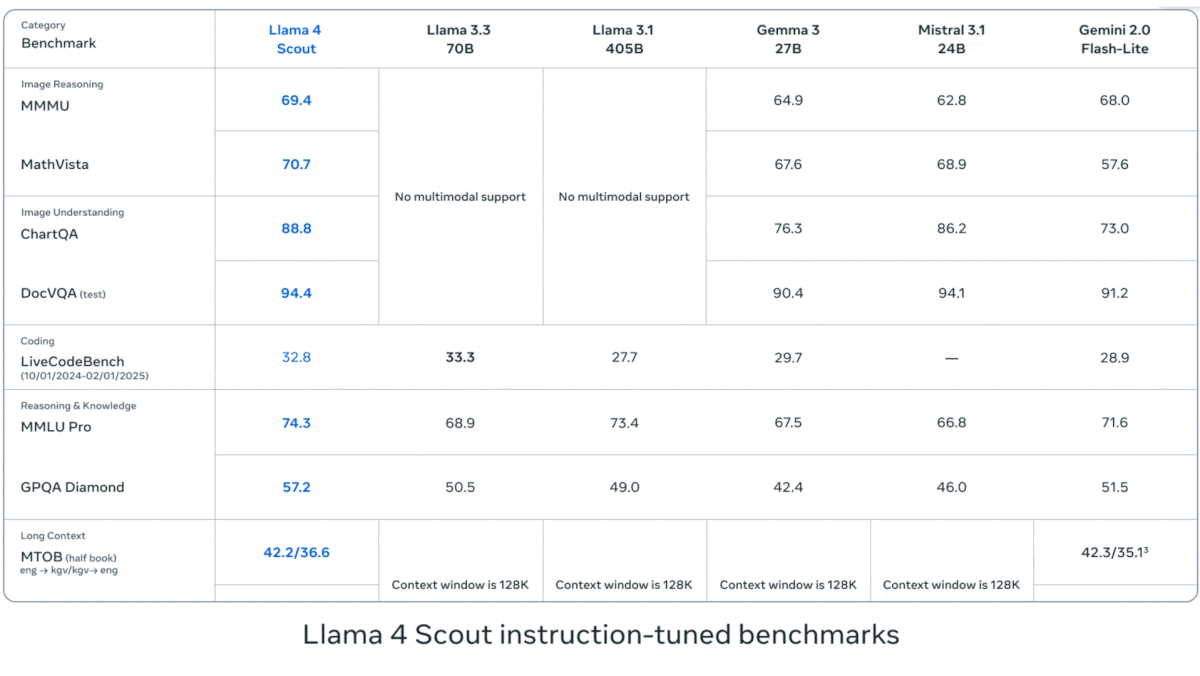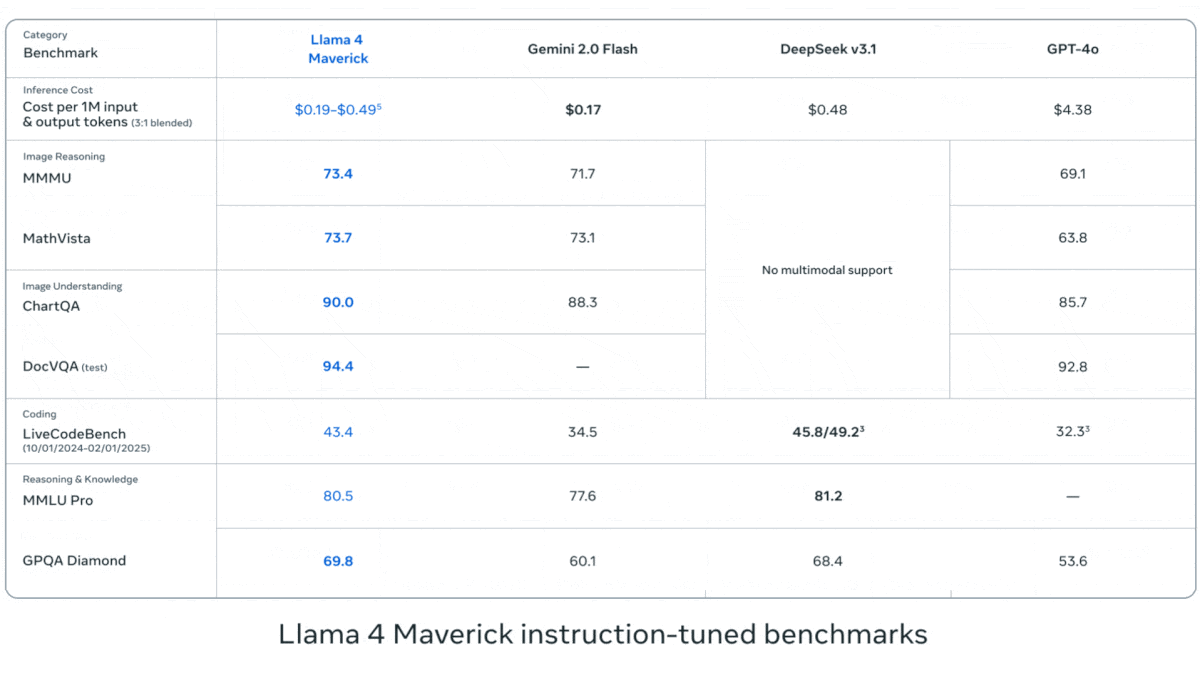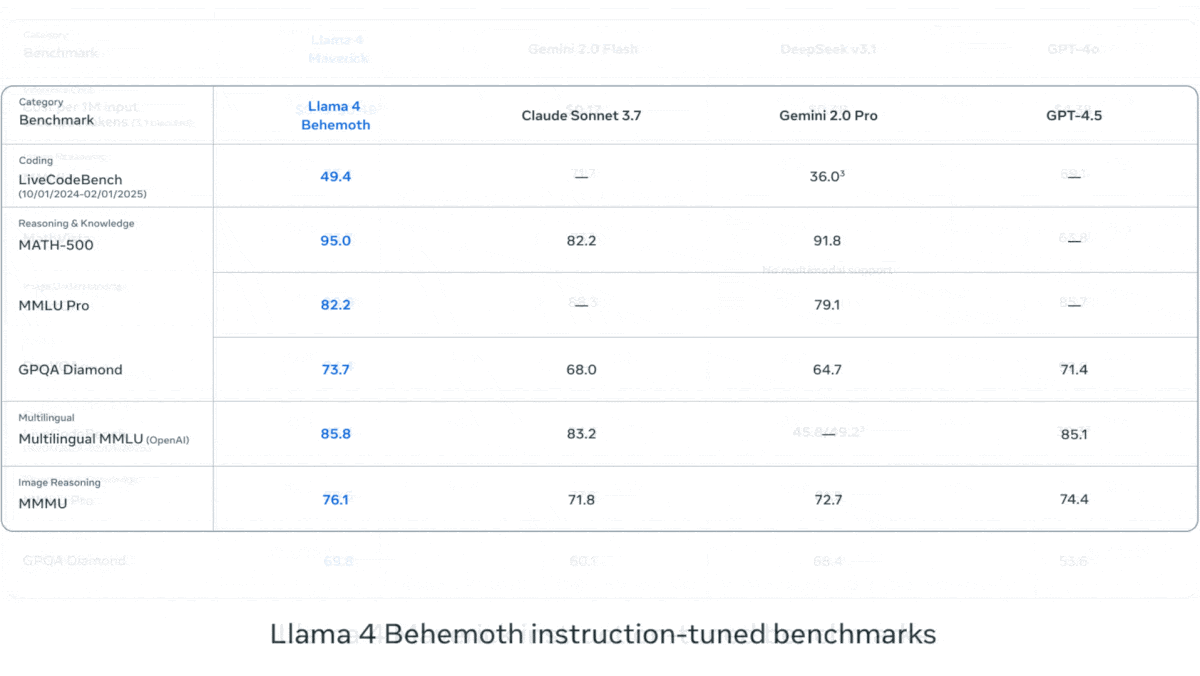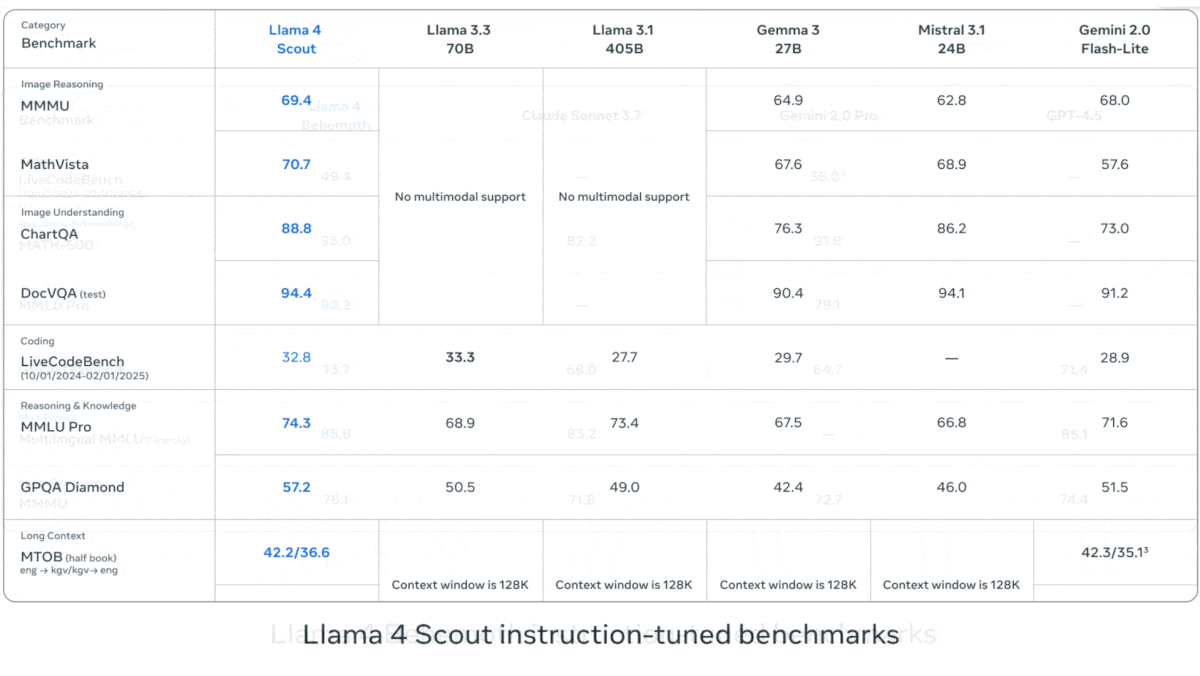
Meta Releases Llama 4 Series Vision-Language Models: Meta launched two open-source multimodal models from the Llama 4 series: Llama 4 Scout (109B parameters, 17B active) and Llama 4 Maverick (400B parameters, 17B active), and previewed the nearly 2T parameter Llama 4 Behemoth. These models all use a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, supporting text, image, and video input, and text output. Scout boasts a context window of up to 10M tokens (though its practical effectiveness is questioned), while Maverick’s is 1M. The models show strong performance on various benchmarks including image, coding, knowledge, and reasoning, with Scout outperforming models like Gemma 3 27B, Maverick surpassing GPT-4o and Gemini 2.0 Flash, and early versions of Behemoth exceeding GPT-4.5. The release further advances the pace of open-source models catching up to closed-source ones (Source: DeepLearning.AI, X @AIatMeta)
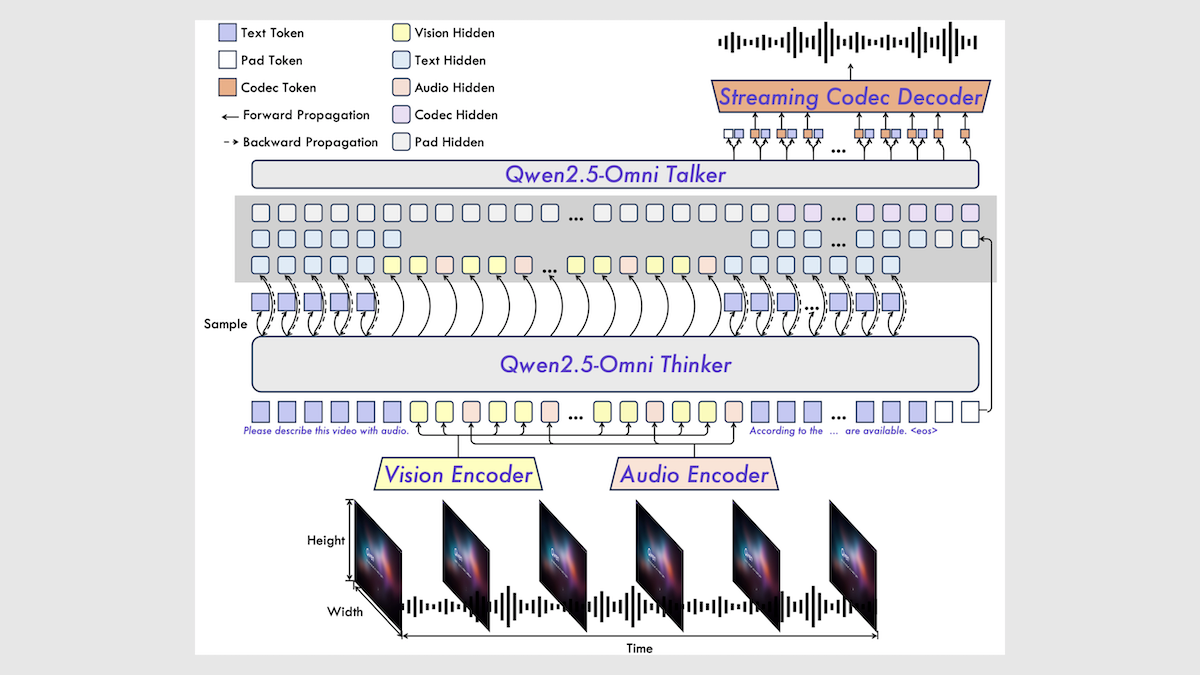
Alibaba Releases Qwen2.5-Omni 7B Multimodal Model: Alibaba released a new open-source multimodal model, Qwen2.5-Omni 7B, capable of processing text, image, audio, and video inputs, and generating text and speech outputs. The model is built upon the Qwen 2.5 7B text model, Qwen2.5-VL vision encoder, and Whisper-large-v3 audio encoder, utilizing an innovative Thinker-Talker architecture. It performs well on multiple benchmarks, achieving SOTA levels particularly in audio-to-text, image-to-text, and video-to-text tasks, though slightly underperforming in pure text and text-to-speech tasks. The release of Qwen2.5-Omni further enriches the selection of high-performance open-source multimodal models (Source: DeepLearning.AI)
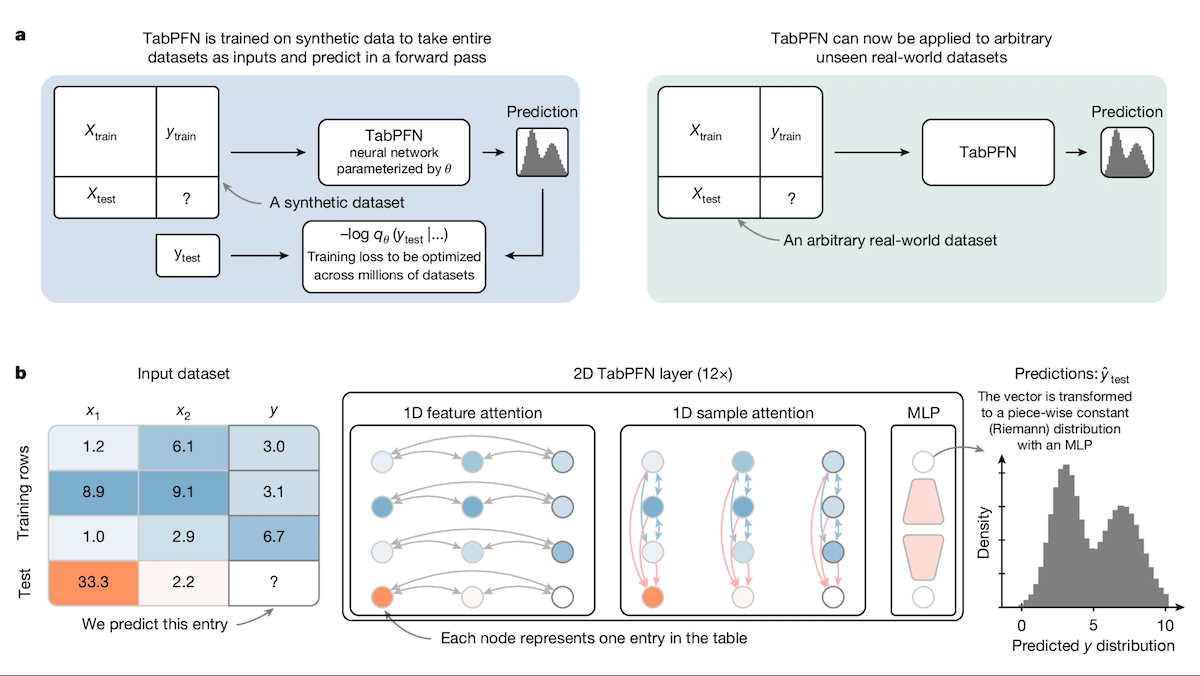
TabPFN: A Transformer for Tabular Data Outperforming Decision Trees: Researchers from the University of Freiburg and other institutions introduced Tabular Prior-data Fitted Network (TabPFN), a Transformer model specifically designed for tabular data. Pre-trained on 100 million synthetic datasets, TabPFN learns to identify patterns across datasets, enabling it to perform classification and regression predictions directly on new tabular data without additional training. Experiments show that on AutoML and OpenML-CTR23 benchmarks, TabPFN outperforms popular gradient boosting tree methods like CatBoost, LightGBM, and XGBoost in both classification (AUC) and regression (RMSE) tasks, although its inference speed is slower. This work opens new avenues for Transformers in the domain of tabular data processing (Source: DeepLearning.AI)
Intel Platform Emerges as a Cost-Effective Option for Large Model All-in-One Machines: With the popularization of open-source models like DeepSeek, large model all-in-one machines have become a popular choice for enterprises to quickly deploy AI. Intel is offering a cost-effective hardware solution by combining its Arc™ gaming GPUs (like the A770) with Xeon® W processors, reducing the price of these machines from the million-yuan level to the hundred-thousand-yuan level. This platform supports not only DeepSeek R1 but also models like Qwen and Llama. Several companies, including Feizhiyun, Sugon, and Cloudpeak, have launched AI all-in-one products or solutions based on this platform for scenarios like knowledge base Q&A, intelligent customer service, financial investment advising, and document processing, meeting the localized AI inference needs of SMEs and specific departments (Source: QbitAI)
Google Introduces 7th Generation TPU “Ironwood”: At the Google Cloud Next conference, Google unveiled its seventh-generation TPU system, Ironwood, optimized specifically for AI inference. Compared to the first-generation Cloud TPU, Ironwood offers a 3,600x performance increase and a 29x improvement in energy efficiency. Relative to the sixth-generation Trillium, Ironwood delivers 2x better performance per watt, features 192GB of memory per chip (6x Trillium’s), and boasts 4.5x faster data access speeds. Ironwood is expected to launch later this year, aiming to meet the growing demand for AI inference (Source: X @demishassabis, X @JeffDean, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Google DeepMind and Gemini Models to Support MCP Protocol: Google DeepMind co-founder Demis Hassabis and Gemini model lead Oriol Vinyals have both indicated support for the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and look forward to developing the protocol with the MCP team and industry partners. MCP is rapidly becoming an open standard for the AI Agent era, aiming to enable different models to understand a unified “service language” for easier invocation of external tools and APIs. This move will allow Gemini models to better integrate into the growing MCP ecosystem, facilitating the construction of more powerful Agent applications (Source: X @demishassabis, X @OriolVinyalsML)
Moonshot AI Releases KimiVL A3B Multimodal Model: Moonshot AI has released the KimiVL A3B Instruct & Thinking models, an open-source (MIT license) series of multimodal large models featuring 128K long context capability. The series includes an MoE VLM and an MoE Reasoning VLM, with only about 3B active parameters. It is claimed to outperform GPT-4o on vision and math benchmarks, achieving 36.8% on MathVision, 34.5% on ScreenSpot-Pro, 867 points on OCRBench, and performing well in long context tests (MMLongBench-Doc 35.1%, LongVideoBench 64.5%). Model weights have been released on Hugging Face (Source: X @huggingface)
Orpheus TTS 3B Released: Multilingual Zero-Shot Voice Cloning Model: The open-source community has released the Orpheus TTS 3B model, a 3 billion parameter multilingual text-to-speech model. It supports zero-shot voice cloning, offers streaming generation with latency around 100ms, and allows guided emotion and intonation for generating human-like speech. The model is released under the Apache 2.0 license, with weights available on Hugging Face, further advancing open-source TTS technology (Source: X @huggingface)
OmniSVG Released: Unified Scalable Vector Graphics Generation Model: A new model named OmniSVG has been proposed, aiming to unify the generation of Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG). Based on Qwen2.5-VL and integrating an SVG tokenizer, the model can accept text and image inputs and generate corresponding SVG code. The project website showcases its powerful SVG generation capabilities. The paper and dataset have been released, but model weights are not yet public (Source: X @karminski3, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
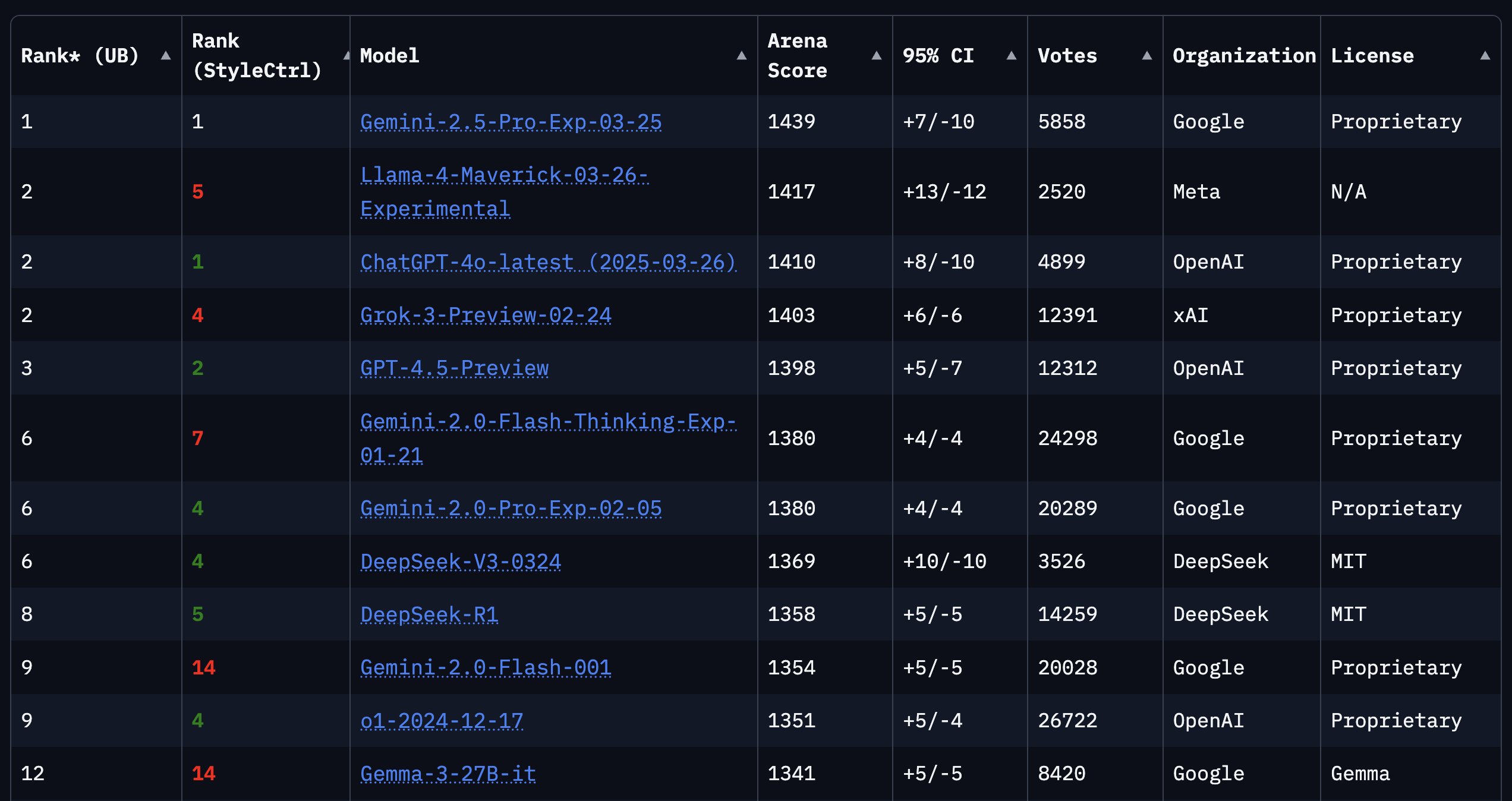
Google Cloud Next 2025 Focuses on AI: The Google Cloud Next conference highlighted advancements in AI. It announced the seventh-generation TPU Ironwood optimized for inference; declared Gemini 2.5 Pro as the currently most intelligent model, topping the Chatbot Arena; combined research from DeepMind, Google Research, and Google Cloud to offer models like WeatherNext and AlphaFold to customers; allowed enterprises to run Gemini models in their own data centers; and announced a partnership with Nvidia to bring Gemini models on-premises via Blackwell and confidential computing (Source: X @GoogleDeepMind, X @GoogleDeepMind, Reddit r/artificial, X @nvidia)
AI Trend Predictions for 2025: Synthesizing various viewpoints, key AI trends for 2025 include: continued development and deeper application of generative AI, increasing importance of AI ethics and responsible AI, proliferation of edge AI, accelerated adoption of AI in specific industries (like healthcare, finance, supply chain), enhancement of multimodal AI capabilities, autonomy and challenges of AI Agents, disruption of traditional business models by AI, and growing demand for diverse AI talent and skills (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon, X @Ronald_vanLoon, X @Ronald_vanLoon)
Tesla Factory Achieves Autonomous Vehicle Transfer: Tesla demonstrated that its manufactured cars can autonomously drive from the production line to the loading area within the factory premises without human intervention. This showcases the application potential of autonomous driving technology in controlled environments (like factory logistics) and represents an advancement of AI in automotive manufacturing and automation (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
🧰 Tools
Free-for-dev: A Curated List of Free Resources for Developers: The ripienaar/free-for-dev project on GitHub is a popular list compiling free tiers of various SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS products useful for developers (especially DevOps and infrastructure developers). The list covers numerous categories including cloud services, databases, APIs, monitoring, CI/CD, code hosting, AI tools, etc., explicitly requiring services to offer a long-term free tier rather than just a trial period, and emphasizing security (e.g., services limiting TLS are not accepted). Driven by the community and continuously updated, this project greatly facilitates developers in finding and comparing free services (Source: GitHub: ripienaar/free-for-dev)
Graphiti: Framework for Building Real-time AI Knowledge Graphs: getzep/graphiti is a Python framework for building and querying time-aware knowledge graphs, particularly suitable for AI Agents needing to process dynamic environmental information. It can continuously integrate user interactions and structured/unstructured data, supporting incremental updates and precise historical queries without needing to fully recompute the graph. Graphiti combines semantic embeddings, keyword search (BM25), and graph traversal for efficient hybrid retrieval, and allows custom entity definitions. The framework is the core technology of the Zep memory layer and is now open-sourced (Source: GitHub: getzep/graphiti)
WeChatMsg: Tool for Extracting WeChat Chat History and Training AI Assistants: LC044/WeChatMsg is a tool for extracting local Windows WeChat chat history (supports WeChat 4.0) and exporting it to formats like HTML, Word, Excel, etc. It aims to help users permanently save chat records and can analyze them to generate annual reports. Furthermore, the tool supports using the user’s chat data to train personalized AI chat assistants, embodying the principle of “my data, my control.” The project provides a graphical user interface and detailed usage instructions (Source: GitHub: LC044/WeChatMsg)
Alibaba Cloud Bailian Launches Full-Lifecycle MCP Service, Creating an Agent Factory: Alibaba Cloud’s Bailian platform has officially launched full platform capabilities for Model Context Protocol (MCP) services, covering the entire lifecycle of service registration, cloud hosting, Agent invocation, and process composition. Developers can directly use official or third-party MCP services hosted on the platform, such as AutoNavi Maps (Gaode) and Notion, or register their own APIs as MCP services through simple configuration (without managing servers). This aims to lower the barrier for Agent development, enabling developers to quickly build and deploy AI Agents capable of calling external tools, promoting the application of large models in real-world scenarios. This service is seen as an important step in Alibaba’s AI commercialization (Source: WeChat Official Account – AINLPer, QbitAI)
Hugging Face Partners with Cloudflare to Offer Free WebRTC Infrastructure: Hugging Face has partnered with Cloudflare to provide enterprise-grade WebRTC infrastructure globally for AI developers via FastRTC. Developers can use their Hugging Face Token to transfer 10GB of data for free, enabling the creation of real-time voice and video AI applications. An official Llama 4 voice chat demo is provided as an example, showcasing the convenience brought by this collaboration (Source: X @huggingface)
Google AI Studio Receives Major UI Update: The user interface of Google AI Studio (formerly MakerSuite) has undergone the first phase of redesign, bringing a more modern look and feel. This update aims to lay the foundation for more developer platform features to be launched in the coming months. The new UI is more consistent with the style of the Gemini app and adds a dedicated developer backend for API and payment management. This update signals an expansion of platform capabilities, potentially including access to new models (like Veo 2) (Source: X @JeffDean, X @op7418)
LlamaIndex Introduces Visual Citation Feature: LlamaIndex released a new tutorial demonstrating how to use the layout Agent feature in LlamaParse to achieve visual citations for Agent answers. This means generated answers can not only be traced back to the text source but also directly mapped to the corresponding visual region (precisely located via bounding boxes) in the source document (e.g., PDF). This enhances the interpretability and traceability of Agent responses, especially useful for processing documents containing charts, tables, and other visual elements (Source: X @jerryjliu0)
LangGraph Launches No-Code GUI Builder: LangGraph now offers a no-code graphical user interface (GUI) builder for designing Agent architectures. Users can plan Agent workflows and node connections through drag-and-drop visual operations, and then generate Python or TypeScript code with a single click. This lowers the barrier to building complex Agent applications, facilitating rapid prototyping and development (Source: X @LangChainAI)
Perplexity Updates Stock Chart Feature: Perplexity has updated its stock chart feature to reflect intraday price changes in real-time, rather than stretching the timeline to fill the entire chart. While basic, this improvement enhances the immediacy and utility of financial information display (Source: X @AravSrinivas, X @AravSrinivas)
OLMoTrace: Tool Connecting LLM Output to Training Data: The Allen Institute for AI (AI2) has launched OLMoTrace, a tool that can map the output of OLMo models back to their corresponding training data sources in real-time (achieving matches within seconds across 4T tokens of data). This helps understand model behavior, improve transparency, and refine post-training data. The tool aims to assist researchers and developers in better understanding the internal mechanisms and knowledge sources of large language models (Source: X @natolambert)
llama.cpp Merges Support for Qwen3 Models: The popular local LLM inference framework llama.cpp has merged support for the upcoming Qwen3 series models, including both base and MoE versions. This means that once the Qwen3 models are released, users will be able to use GGUF-formatted quantized models within the llama.cpp ecosystem immediately, facilitating running them on local devices (Source: X @karminski3, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
KTransformers Framework Supports Llama 4 Models: The Chinese AI inference framework KTransformers (known for supporting CPU+GPU hybrid inference, especially MoE model offloading) has added experimental support for Meta’s Llama 4 series models in its development branch. According to the documentation, running the Q4 quantized Llama-4-Scout (109B) requires approximately 65GB RAM and 10GB VRAM, while Llama-4-Maverick (402B) needs about 270GB RAM and 12GB VRAM. On a 4090 + dual Xeon 4 configuration, single-batch inference speed can reach 32 tokens/s. This provides a possibility for running large MoE models with limited VRAM (Source: X @karminski3, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
LangChain Integrates xAI Grok 3 Model: LangChain announced that it has integrated xAI’s newly released Grok 3 model. Users can now call Grok 3 through the LangChain framework to build applications leveraging its powerful capabilities (Source: X @LangChainAI)
n8n Cloud Service Free Deployment Tutorial: Describes how to use Hugging Face Spaces and Supabase to deploy the open-source workflow automation platform n8n for free, obtaining public domain access with HTTPS support. This allows users to utilize n8n’s full functionality (including nodes requiring callback URLs) without purchasing servers and configuring domains and SSL certificates themselves. The method leverages Supabase’s free database to solve the data loss issue caused by Hugging Face Space hibernation (Source: WeChat Official Account – 袋鼠帝AI客栈)
OpenWebUI Plugin Updates: Context Counter & Adaptive Memory: Community developers released/updated two plugins for OpenWebUI: 1) Enhanced Context Counter v3, providing a detailed dashboard for token usage, cost tracking, and performance metrics, supporting various models and custom calibration. 2) Adaptive Memory v2, dynamically extracting, storing, and injecting user-specific information (facts, preferences, goals, etc.) via an LLM to achieve personalized, persistent, and adaptive conversational memory, running entirely locally without external dependencies (Source: Reddit r/OpenWebUI, Reddit r/OpenWebUI)
QuickVoice MCP: Let Claude Make Phone Calls: A community developer created an MCP (Model Context Protocol) tool called QuickVoice that allows MCP-enabled models like Claude 3.7 Sonnet to make and handle real phone calls. Users can instruct the AI with natural language (e.g., “Call the doctor to make an appointment”) to complete the call task, including navigating IVR menus. The project is open-sourced on GitHub (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
RPG Dice Roller for OpenWebUI: The community developed an RPG dice roller tool plugin for OpenWebUI, convenient for getting authentic random results during role-playing game conversations (Source: Reddit r/OpenWebUI)
📚 Learning
Girafe-ai Open-Source Machine Learning Course: The girafe-ai/ml-course project on GitHub provides teaching materials for the first semester of the girafe-ai machine learning course, covering topics like Naive Bayes, kNN, Linear Regression/Classification, SVM, PCA, Decision Trees, Ensemble Learning, Gradient Boosting, and an introduction to Deep Learning. Lecture video recordings, PPT slides, and assignments are available. A valuable resource for learning fundamental machine learning concepts (Source: GitHub: girafe-ai/ml-course)
USTC and Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab Propose CMO Framework to Optimize Chip Logic Synthesis: Professor Wang Jie’s team at the University of Science and Technology of China, in collaboration with Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab, published a paper at ICLR 2025 proposing CMO, an efficient logic optimization method based on neuro-symbolic function mining. The framework uses Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to guide Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), generating lightweight, interpretable, and generalizable symbolic scoring functions to prune invalid node transformations in logic optimization operators (like Mfs2). Experiments show CMO can improve the runtime efficiency of critical operators by up to 2.5x while maintaining optimization quality, and has been applied in Huawei’s self-developed EMU logic synthesis tool (Source: QbitAI)
Shanghai AI Lab Proposes MaskGaussian, a New Gaussian Pruning Method: Researchers at Shanghai AI Lab presented the MaskGaussian method at CVPR 2025 for optimizing 3D Gaussian Splatting. By incorporating learnable mask distributions into the rasterization process, this method, for the first time, preserves gradients for both used and unused Gaussian points simultaneously. This allows for pruning a large number of redundant Gaussians while maximally preserving reconstruction quality. Experiments on multiple datasets pruned over 60% of Gaussians with negligible performance loss, while also improving training speed and reducing memory footprint (Source: QbitAI)
Qwen2.5-Omni Technical Report Analysis: A Reddit user shared detailed notes analyzing Alibaba’s Qwen2.5-Omni technical report. The report introduces the model’s Thinker-Talker architecture, its multimodal (text, image, audio, video) input processing methods (including the innovative TMRoPE positional encoding for audio-video alignment), streaming speech generation mechanism, training pipeline (pre-training + post-training RL), etc. These notes provide valuable insights into the inner workings of this cutting-edge multimodal model (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
McKinsey Releases Playbook for Scaling Generative AI in Enterprises: McKinsey has published a playbook for data leaders discussing how to scale the application of generative AI within enterprises. The report likely covers aspects such as strategy formulation, technology selection, talent development, and risk management, providing guidance for businesses to implement and expand GenAI in practice (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
Beginner’s Guide to Learning AI Agents: Khulood_Almani shared resources or steps on how to start learning about AI Agents, potentially including learning paths, key concepts, recommended tools or platforms, offering guidance for learners wanting to enter the field of AI Agents (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
Study on Re-Ranking Techniques in Visual Place Recognition: A paper on arXiv explores whether re-ranking techniques are still effective in the task of Visual Place Recognition (VPR). The research likely analyzes the pros and cons of existing re-ranking methods and evaluates their role and necessity in modern VPR systems (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning, Reddit r/MachineLearning)
“AI 2027” Research Report Explores ASI Risks and Future: A research report titled “AI 2027” discusses potential AI development scenarios by 2027, particularly the possibility of automated AI R&D leading to the emergence of Artificial Superintelligence (ASI). The report analyzes potential risks posed by ASI, such as human disempowerment due to goal misalignment, power concentration, international arms races exacerbating security risks, model theft, and lagging public perception. It also explores potential geopolitical outcomes like war, treaties, or capitulation (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
Research on Neural Network Activation Alignment: A paper published on OpenReview investigates the reasons behind representational alignment in neural networks. The study finds that alignment does not originate from individual neurons but is related to how activation functions work, proposing the Spotlight Resonance Method to explain this phenomenon and providing experimental support (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)
💼 Business
Alibaba International Focuses on AI for Breakthrough: Facing fierce competition in the cross-border e-commerce industry and global trade shifts, Alibaba International Digital Commerce Group views AI as a core strategy, investing heavily to seek growth and efficiency improvements. The company launched the “Bravo 102” global AI talent training program and designated 80% of campus recruitment positions as AI-related. AI applications already cover B2B (AI search engine Accio, “Business Assistant” AI Agent) and B2C (Aidge platform providing virtual try-on, AI customer service, etc.). Although Alibaba International’s revenue grew significantly (up 32% YoY in 2024 Q4), investments led to increased losses. AI is seen as the key driver for Alibaba International to move beyond low-price competition, achieve high value-added transformation, and refine operations (Source: 36Kr)
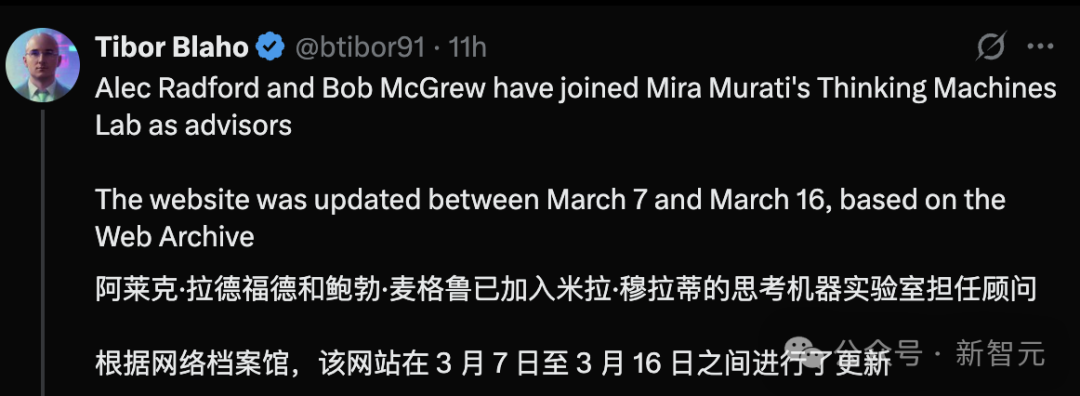
Former OpenAI Core Members Join Mira Murati’s New Company: Alec Radford, the first author of the original GPT paper, and Bob McGrew, former VP of Research at OpenAI, have joined Thinking Machines Lab, the new AI company founded by former OpenAI CTO Mira Murati, as advisors. Radford played a crucial role in the birth of the GPT series models, while McGrew was deeply involved in the development of GPT-3/4 and the o1 model. A significant number (at least 19) of Thinking Machines Lab’s founding team members come from OpenAI. The company aims to popularize AI applications and is reportedly planning to raise $1 billion at a $9 billion valuation, indicating high market expectations for startups led by top AI talent (Source: Xin Zhi Yuan)
Mutual Funds Focus on AI + Healthcare Business of Pharmaceutical Companies: Recently, several Chinese mutual funds have intensively researched listed pharmaceutical companies, with AI applications in the medical field becoming a key focus. Haier Biomedical introduced its AI applications in IoT blood networks and vaccine networks, as well as progress in using AI to improve efficiency in public health scenarios (like vaccine appointments). Hisun Pharma stated it has adopted the DeepSeek-R1 model and is collaborating with AI pharmaceutical companies, hoping to empower the entire new drug R&D process with AI. Kanion Pharmaceutical also indicated it is building an AI + multi-omics driven platform for innovative traditional Chinese medicine discovery. This shows that the application of AI technology in pharmaceutical R&D, operations, and patient services is receiving significant attention from the capital market (Source: ChiNext Observer)
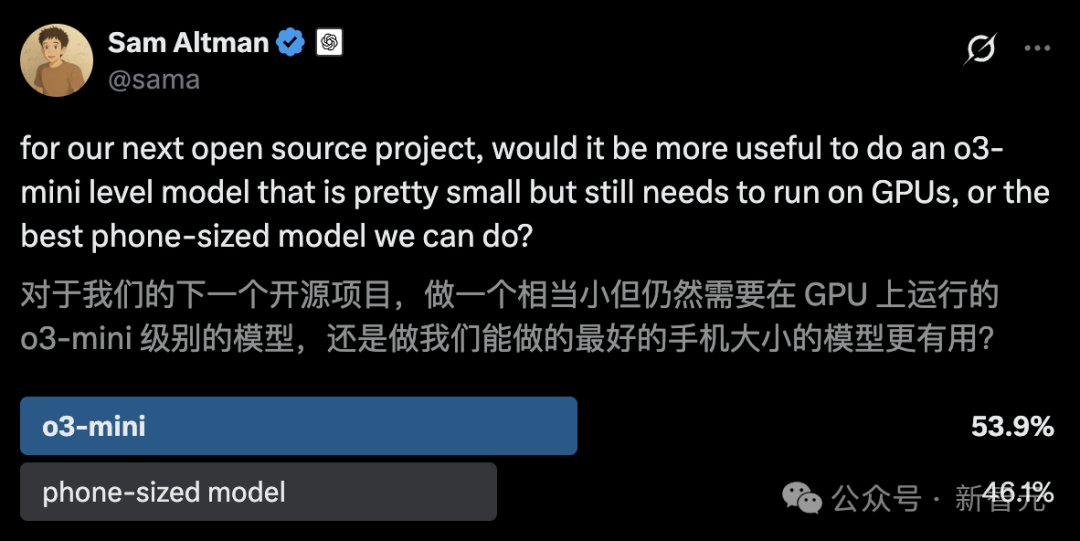
OpenAI Launches Pioneers Program to Deepen Industry Collaboration: OpenAI has launched the Pioneers program, aiming to establish partnerships with ambitious companies to co-build advanced AI products. The program will focus on two aspects: first, intensive fine-tuning of models to outperform general models on high-value tasks in specific domains; second, building better real-world evaluations (evals) so the industry can better measure model performance on domain-relevant tasks. This indicates OpenAI is seeking to apply its technology more deeply into specific industries and enhance the practicality and evaluation standards of models in vertical domains through collaboration (Source: X @sama)
Nvidia and Google Cloud Partner to Enable On-Premises Gemini Deployment: Nvidia and Google Cloud announced a collaboration to support running Google’s Gemini models on-premises within enterprises. The solution will combine the Nvidia Blackwell GPU platform and Confidential Computing technology, aiming to provide enterprises with high-performance and secure localized AI deployment options. This move addresses the needs of some enterprises regarding data privacy, security compliance, and specific performance requirements, allowing them to run powerful Gemini models on their own infrastructure (Source: X @nvidia)
Google Allows Enterprises to Run Gemini Models in Their Own Data Centers: Google Cloud announced that it will allow enterprise customers to run its Gemini AI models in their own data centers. This initiative aims to meet enterprise demands for data sovereignty, security, and customized deployment, enabling them to leverage Gemini’s powerful capabilities within their local environments without transmitting sensitive data to the cloud. This offers greater flexibility and control for businesses, especially in highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang Downplays Tariff Impact, AI Servers May Be Exempt: Facing potential new US tariff policies, Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang stated the impact would be limited and suggested that most of Nvidia’s AI servers might receive exemptions. This could be due to the strategic importance of their products or specific trade classifications. This news is a positive signal for the AI industry reliant on Nvidia hardware, helping to alleviate concerns about rising supply chain costs (Source: Reddit r/artificial, Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence)
🌟 Community
Reddit Buzz: When Will Qwen3 Models Be Released?: The Reddit community and users on X (formerly Twitter) are actively discussing the release date of Alibaba’s Qwen3 models. Although some users shared posters from an Alibaba AI summit speculating an imminent release, it was later confirmed that Qwen3 was not announced at that summit. Meanwhile, the news of llama.cpp merging support for Qwen3 has heightened community anticipation. This reflects the high level of attention and expectation surrounding the progress of Chinese large models within the open-source community (Source: X @karminski3, Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Reasoning Dataset Competition Launched: Bespoke Labs, in collaboration with Hugging Face and Together AI, has launched a reasoning dataset competition. The goal is to encourage the community to create more diverse reasoning datasets that better reflect real-world complexity, especially in multi-domain reasoning (e.g., finance, medicine), to drive the development of next-generation LLMs. Existing datasets (like OpenThoughts-114k) have played an important role in model training, and the competition hopes to further push the boundaries of datasets (Source: X @huggingface)
LiveCodeBench Programming Benchmark Updated, o3-mini Leads: The LiveCodeBench programming ability leaderboard has been updated after 8 months, with OpenAI’s o3-mini (high) and o3-mini (medium) taking the first and second spots, respectively, and Google Gemini 2.5 Pro ranking third. The list sparked community discussion, with some users questioning the relatively lower rankings of Claude 3.5/3.7, feeling it doesn’t align with their actual usage experience. This reflects potential discrepancies between different benchmarks and users’ subjective perceptions (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Community Discusses Claude Code: Powerful but Expensive and Buggy: Reddit users discussing Anthropic’s Claude Code generally agree it has strong context awareness and good coding performance, even feeling “like it’s from the future.” However, its drawbacks include high cost (one user reported daily spending up to $30) and some bugs (like claude.md files disappearing after sessions, syntax errors in output). Users look forward to more capable and affordable alternatives in the future (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
User Shares Quantized Mistral-Small-3.1-24B Models: An Ollama community user shared Q5_K_M and Q6_K quantized versions (GGUF format) of the Mistral-Small-3.1-24B model, filling the gap as the official repository only offered Q4 and Q8. These quantized models were created using the Ollama client, support vision capabilities, and provide context length references on an RTX 4090 (Source: Reddit r/LocalLLaMA)
Community Seeks AI Video Upscaling Tool: A Reddit user asked if there exists an AI tool capable of upscaling 240p low-resolution videos to 1080p/60fps, hoping to restore old music videos. Comments mentioned tools like Ai4Video and Cutout.Pro, but some opinions suggested that upscaling from extremely low resolution might yield limited results, potentially resembling regeneration more than restoration (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
User Suspects Claude 3.5 Sonnet Was Stealthily Updated: A developer on Reddit suspects, based on usage experience (e.g., model starting to use emojis, changes in response style), that Anthropic silently replaced the original Claude 3.5 Sonnet model with an optimized or distilled version without notification, leading to changes in performance or behavior. The user believes the original 3.5 was superior to 3.7 for coding but has experienced a decline recently. This sparked community discussion about model version transparency and consistency (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
Anthropic Report Sparks Discussion on Student AI Cheating: Anthropic released an education report analyzing millions of anonymized student conversations, finding that students might be using Claude for academic misconduct. The report triggered community discussion with viewpoints including: student cheating has always existed, AI is just a new tool; the education system needs to adapt to the AI era, assessment methods should change; some users expressed privacy concerns about Anthropic analyzing user conversation data (Source: Reddit r/ClaudeAI)
Users Discuss Monitoring Methods for LLM/Agent Applications: Users in the Reddit Machine Learning community initiated a discussion asking how others monitor the performance and cost of their LLM applications or AI Agents, such as tracking token usage, latency, error rates, prompt version changes, etc. The discussion aims to understand community practices and pain points in LLMOps, whether using custom solutions or specific tools (Source: Reddit r/MachineLearning)
💡 Other
Andrew Ng Comments on US Tariff Policy’s Impact on AI: In his weekly newsletter The Batch, Andrew Ng expressed concerns about the new US tariff policy, arguing it not only harms alliances and the global economy but also indirectly hinders US domestic AI development and application adoption by restricting hardware imports (like servers, cooling, networking equipment, power facility components) and increasing consumer electronics prices. He noted that while tariffs might slightly stimulate demand for robotics and automation, this isn’t an effective solution for manufacturing issues, and AI progress in robotics is relatively slow. He called for the AI community to strengthen international cooperation and idea exchange (Source: DeepLearning.AI)
Breakthroughs and Pitfalls of AI in Telecom: An article explores the potential of artificial intelligence in the telecommunications industry, such as network optimization, customer service, predictive maintenance, etc., while also pointing out potential challenges and pitfalls, like data privacy, algorithmic bias, integration complexity, and impact on existing workflows (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
Skill Diversity Crucial for AI Return on Investment: Antonio Grasso emphasizes that achieving a return on investment (ROI) for artificial intelligence projects requires teams with diverse skill sets, potentially including data science, engineering, domain knowledge, ethics, business analysis, and more (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
AI-Powered Supply Chains Lead Sustainable Development: Nicochan33’s article points out that using AI to optimize supply chain management (e.g., route planning, inventory management, demand forecasting) not only improves efficiency but also promotes sustainable development goals by reducing waste, lowering energy consumption, etc. (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
Autonomy, Safeguards, and Pitfalls of AI Agents: A VentureBeat article discusses key issues in AI Agent development, including how to balance their autonomous capabilities, design effective safeguards to prevent misuse or unintended consequences, and potential pitfalls encountered during deployment and use (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
AI Seen as Biggest Threat to ‘Boring’ Businesses: A Forbes article argues that artificial intelligence poses the greatest disruptive threat to businesses traditionally considered “boring” or process-driven, as these often involve numerous tasks that can be automated or optimized by AI (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
Bias Problem in Medical Algorithms and New Guidelines: A Fortune article focuses on the long-standing issue of bias in AI within the healthcare sector and explores whether new guidelines can help address this problem, ensuring fairness and accuracy in AI medical applications (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
AI’s Role in Workforce Upskilling and Disease Identification: A Forbes article explores the positive roles of AI in two areas: first, helping to upskill the existing workforce to adapt to future job demands, and second, providing support in early disease identification and diagnosis (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
AI Digital Agents Will Redefine Work: A VentureBeat article discusses how AI Agents (digital agents) will integrate into the workplace, not just as tools, but potentially changing the very definition of work, processes, and human-machine collaboration (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
The Invisible, Autonomous, and Attackable Dilemma of AI Agents: A VentureBeat article delves into the new dilemmas posed by AI Agents: their operation can be “invisible” to users, they possess high autonomy, and they can also be maliciously exploited or attacked, presenting new challenges for security and ethics (Source: X @Ronald_vanLoon)
Trump Threatens 100% Tariff on TSMC: Former US President Trump stated he had told TSMC that if it didn’t build factories in the US, its products would face a 100% tariff. This remark reflects the ongoing impact of geopolitics on the semiconductor supply chain and could pose potential risks to the supply of AI hardware dependent on TSMC chips (Source: Reddit r/ArtificialInteligence, Reddit r/artificial)
Google Gemini 2.5 Pro Reportedly Missing Key Safety Report: Fortune reported that Google’s latest Gemini 2.5 Pro model is missing a crucial safety report (Model Card), potentially violating AI safety commitments Google previously made to the US government and international summits. This incident raises concerns about transparency and the fulfillment of safety commitments by large tech companies regarding model releases (Source: Reddit r/artificial)
Using AI for License Plate Recognition: Rackenzik’s article introduces deep learning-based license plate detection and recognition technology, discussing challenges such as image blur, variations in license plate styles across different countries/regions, and difficulties in recognition under various real-world conditions (Source: Reddit r/deeplearning)